Types and features of DNA microarrays
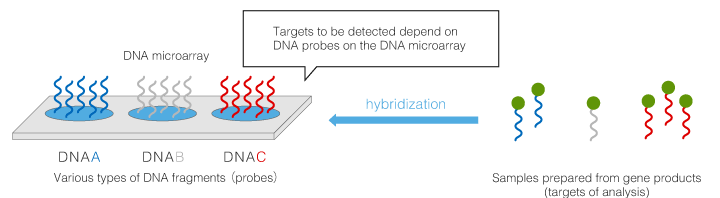
By hybridizing nucleic acid targets including DNA and RNA extracted from a specimen to a DNA microarray, various statuses of DNA and RNA can be analyzed, including determination of nucleic acid sequences of the targets, analysis of gene mutations, measurement of expression levels and copy number of genes, and analysis of methylation status.
DNA microarrays are roughly divided into the types below. 3D-Gene® is an oligo DNA microarray.
Main types of DNA microarrays
| Oligo DNA microarrays (3D-Gene®) |
An oligo DNA microarray is a DNA microarray whose probe is the chemically synthesized oligo DNA after genes corresponding to exons in the region of 20-100 nts are selected. Since the probe is shorter than a cDNA microarray, its specificity is high and cross hybridization can be inhibited. |
|---|---|
| cDNA microarrays | A cDNA microarray consists of a collection of cDNA fragments which are reverse transcripts of gene transcription products (mRNA). These cDNA fragments are immobilized on a substrate. The probes are the cDNA fragments previously adjusted according to the PCR method. A cDNA microarray is produced by spotting the fragments on the substrate using a spotter. The lengths of cDNA are generally not uniform. Nucleic acid probes for detection can be spotted ranging from a few hundred nts (nucleotides) to over a thousand nts. |
| BAC clone chips | A BAC clone chip is a DNA microarray whose probe is a template amplified by PCR. The template is a genome region incorporated into a comprehensive BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) clone which various research institutions used in decoding the genome sequence of various organisms. BAC is a vector that can clone a gene of 100-300 kb long. A BAC clone chip is used to analyze the number of genomic DNA copies in such methods as the CGH array. |

