One-color method
Presently, the methods used in hybridization of DNA microarray are largely divided into the one-color and two-color fluorescence methods. The selection of method affects the experimental design. In many cases, the measurement method that can be used is determined by the types of DNA microarray. Therefore, please confirm the applicable measurement method with the manufacturer and supplier before the experiment. The names of one-color and two-color fluorescence methods originate from the types of fluorescent dyes used in labeling. A single fluorescent dye is used in the one-color method, and two types of fluorescent dyes are used for the two-color method.
In the one-color method, one type of target sample is hybridized on one DNA microarray. In the two-color method, two types of target samples are hybridized competitively on one DNA microarray.
Outlines of one-color and two-color methods will be presented below. For simplicity, the examples illustrated involve an experiment on two groups to compare the effects of drugs on cultured cells. The groups were a non-treated group (Group A, sample a) and a treated group (Group B, sample b).
One-color method
Target samples a and b are labeled with one type of dye in the one-color method. Then each sample is hybridized on a separate DNA microarray. The advantage of the one-color method is the ease of designing an experimental plan. Even if the number of samples to be analyzed increases suddenly, it is often not problematic for the one-color method.
A reference target sample (reference) needs to be prepared for comparison in the two-color method. The selection of the one-color method might be prudent if the amount of increase in the sample number is unknown. The disadvantage of the one-color method is the following. Since data among multiple DNA microarrays are used, variation of the DNA microarrays themselves could affect the results. In the two-color method, the same DNA microarray is used for comparison. Therefore, a problem of variation is minimal.
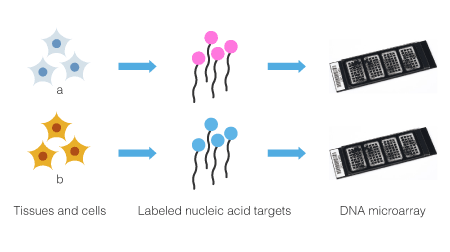
Target samples a and b are labeled with one type of dye in the one-color method.
Then each sample is hybridzed on a separate DNA microarray.

Comparison is performed among multiple DNA microarrays.
- Advantage
- It's easy to design an experimental plan.
- Disadvantages
- The variation of the DNA microarrays themselves could affect the results.
* For any requested information for 3D-Gene®, please contact us.

